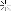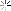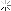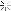کد:
http://www.isaserver.org/tutorials/Using_ISA_dial_on_demand_for_Internet_connections.html
This tutorial will cover the outline about using ISA dial-on-demand, reasons and various scenarios where dial-on-demand ISA technology can be used. I will also show you how to set alerts to ensure that this technology does not fail you or your organization. In mission critical environments where internet is a vital resource it may prove necessary to utilize this untapped ISA feature.
In certain environments where a permanent connection to the internet is not required, it might be useful to connect to the internet using ISA’s dial on demand capabilities. One can use the dial on demand capabilities of ISA to connect to the Internet to save on dialup cost in regions of the world where local telephone calls analog or ISDN (integrated services digital network) are not free. (This is the case for most developing countries). If you are running a small to medium size business, and are trying to cut costs, and if you are very concerned about your telephone bill. You might consider this approach. I have found this scenario to very useful in Lab setups when evaluating and testing ISA.
In order to dial-up to the internet using dial-on-demand technology both and active dial-up entry and a routing rule that makes use of the active dial-up entry must exist. Remember to check the check box in the routing rule that uses the active dial-up entry.
The following are scenarios where ISA can be used to dial-on-demand.
Warning the scenarios below can cost vast amounts of money if not configured correctly and if used in scenarios that are incorrectly assessed.
- Internet connection: when a request is made by an ISA client and a routing rule exists that enables ISA to use the default or active dial-up entry, to establish the dial-up connection to the Internet so that the client request can be quenched.
- Upstream Firewall chaining and backup route: when a request is made and you have specified a primary route that uses another ISA server that is at different site, and the site is only available over dial-up, and the default or active dial-up is used to connect to the remote ISA machine to quench the request. Warning:!!! This scenario should only be used with discretion and in small environments as high phone bills can be rung up in a matter of minutes. What can happen is that many very small requests can be made within an hour and each time (depending on the telephone network) that you dial the remote site a cost is incurred. If you make 25 requests at 5c each within 5 minutes you will be spending $15 an hour. If this is ISDN you can easily double that figure. Some companies use 4 ISDN lines this means that the total amount will be 4 x $30 = $120/hour Please note this. I have witnessed cases of $3800 a day when someone forgot that their download might take the whole weekend.
- Caching: Active caching can be configured to dial-up to the internet to retrieve the most commonly used files.
Understanding when the dial-up connection terminates
ISA Server drops the dial-up connection if it encounters the following criteria.
- When other dial-up entry are made active. Or active entry is modified.
- The main route comes back online ( the backup or dial-up route is then no longer needed)
- When dial-up entry for the backup route or Firewall chaining is disabled.
- When manual intervention is performed on ISA server.
You should also note that it can happen if the respective routing rule exists that DNS requests can also cause ISA to dial-up in order to resolve the internet requests. Also note that if ISA can not identify the request or match it to a corresponding policy ISA will also dial-up in order to resolve the request. Note that access policies and routing rules determine how and if a client request is let through to the internet.
Controlling the way ISA Server dials-up
• Make sure that your LDT (local domain table) is configured in such a way that it contains the computers on your LAN/WAN, this prevents ISA from dialing up unnecessarily for DNS requests. The LDT determines if name resolution should be handled by ISA for the local LAN or if the request should be sent to a DNS server that resides externally on the internet.
• Control how clients access the internet and when they access the internet, by restricting their access with site and content rules and applying a specific schedule to the site and content rule. Using this method you can control the amount of internet requests sent out. Any request sent at a time that does not comply with the schedule within the site and content rule will be denied. Apply this methodology to protocol rules also if you so wish.
Alerts
You can configure an alert that is built into ISA server to let know that there has been a Dial-up failure, via e-mail and you can also configure ISA server to stop or restart services if need be, or run an application or batch file.
1. The diagram above displays where the alerts object can be found within the ISA MMC. Click on alerts.
2. Now double click the Dial-on-demand failure object line.
3. Ensure that the alert is enabled under the general Tab. Then click the Events tab.
4. In order to stop the Alert from multi mailing, you might want to set the number of occurrences before the alert is issued check box to 3. If you are running a mission critical environment I recommend that you do not set this box as you would want to be alerted immediately. Then click on the actions Tab.

5. Within this tab you can configure the IP address of a SMTP (simple mail transfer protocol server) where from you can relay mail off. You can also configure the e-mail address of the person you wish to contact if your Dial-on-demand is not functioning. If you are running a mission critical environment you can Cc or carbon copy the name of an SMS Short Message Service gateway where from you can get ISA to send a mail to your cellular phone 24/7. Please test this before commissioning, as not testing may result in this service not functioning the way it is intended. In this screen you can also choose to run an application or batch files. You can write a simple batch file that restarts your ISA server if it needs to be restarted automatically. You can also stop or start specific services automatically on event that the alert is issued, this can prove to be a powerful tool.
Note: If the SMTP server resides outside your LAN a SMTP packet filter should exist to allow mail relay.
Summary: In this tutorial I have demonstrated how to set up an alert that will mail you if your ISA servers dial-on-demand facility is not functioning as intended. Other tutorials on the Isaserver.org website will help you in creating Routing rules and dial-up entries and setting them active if you get stuck. I have also given you various examples of where this technology can be used. I strongly believe that if you rely heavily on your ISA server for your internet connection you should always set up a back-up route to the internet, be it a back-up route to another ISA server at another site on your WAN or a dial-on-demand route to an ISP or another ISA server at a remote site with an internet connection


 LinkBack URL
LinkBack URL About LinkBacks
About LinkBacks